Blog
Sloth Fever Virus: A Hidden Zoonotic Threat
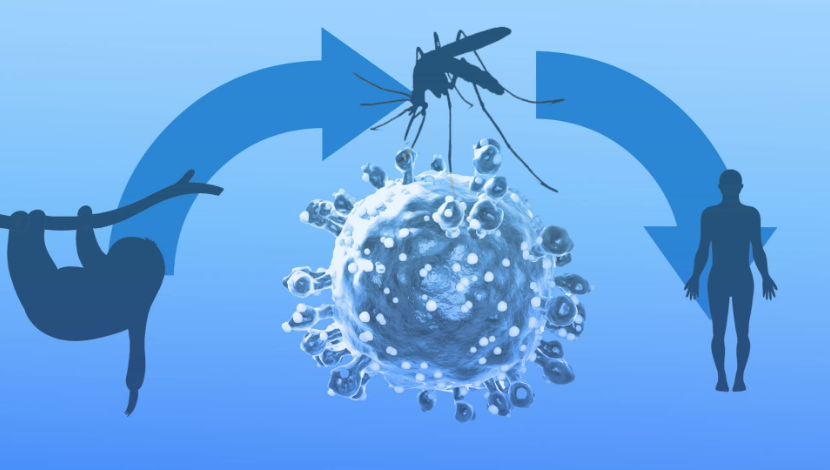

The sloth fever virus is an emerging zoonotic disease, sparking global concern about its potential to jump from wildlife to humans. This virus, primarily found in sloths, has recently made headlines due to sporadic outbreaks in tropical regions. With its potential to affect both animals and humans, it is crucial to understand its origin, transmission, and the steps necessary to prevent a larger outbreak. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the sloth fever virus, its symptoms, its impact on wildlife, and how experts are addressing this public health threat.
What is the Sloth Fever Virus?
The sloth fever virus is a relatively new and under-researched viral strain, possibly zoonotic, meaning it can jump from animals to humans. This virus is associated with fever in sloths, a condition that hasn’t been widely documented until recent years. Though there are concerns that the virus might cause a sloth disease outbreak, further studies are required to fully understand its transmission and impact.
Transmission and Spread of Sloth Fever Virus
Like many zoonotic viruses, the sloth fever virus transmission is believed to occur through close contact with infected animals. Sloths, due to their proximity to humans in certain regions and their interaction with other wildlife, could serve as vectors for spreading the disease.
- Animal-to-human transmission: Close handling of sloths in wildlife sanctuaries or illegal pet trading may increase the risk of this virus being passed to humans.
- Wildlife disease outbreak: The virus could spread quickly among sloth populations, posing risks of widespread sloth-borne illness.
What Makes the Sloth Fever Virus Unique?
What sets the sloth fever virus apart from other wildlife-borne diseases is its relatively long incubation period, which could allow the virus to spread unnoticed in its early stages. This, combined with the fact that sloths are often in close contact with other wildlife, makes containment especially difficult.
| Key Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Incubation Period | Longer than typical zoonotic viruses, making early detection difficult |
| Primary Host | Sloths in tropical regions |
| Transmission | Possible animal-to-human transmission |
| Outbreak Risk | High in sloth-endemic regions |
Symptoms of Sloth Fever
Recognizing sloth fever symptoms is crucial for early detection and containment. While sloths themselves may exhibit milder symptoms, humans infected by the virus could experience more severe effects. Below is a list of common symptoms observed in animals and humans:
Symptoms in Sloths:
- Mild fever
- Lethargy
- Reduced appetite
- Slowed movements (which can be difficult to detect due to their naturally slow nature)
Symptoms in Humans:
- High fever
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Respiratory issues
- In severe cases, inflammation of internal organs
Due to the slow nature of the disease in sloths, symptoms may not be evident for several weeks, increasing the risk of wider spread.
Transmission: How the Virus Spreads
The transmission of the sloth fever virus can occur through direct contact with infected sloths or their bodily fluids. Since sloths inhabit dense rainforests, they are often in close contact with other species, raising the potential for cross-species transmission.
How Does Animal-to-Human Transmission Occur?
Like many zoonotic viruses, sloth fever could spread to humans through:
- Direct contact with sloths, especially those who are sick.
- Infected feces or urine, which can carry viral particles.
- Bites or scratches from infected sloths.
The long incubation period further complicates transmission tracking, as both sloths and other infected wildlife may appear asymptomatic for extended periods.
Is Sloth Fever Zoonotic?
The growing concern among scientists is the zoonotic potential of the sloth fever virus. Zoonotic diseases, those capable of jumping from animals to humans, have become more prevalent due to increased human-wildlife interactions. Studies on the epidemiology of sloth-related viruses indicate a rising risk, especially in regions where humans encroach on sloth habitats.
The Zoonotic Connection
Although there are no confirmed large-scale human infections, small outbreaks in wildlife suggest that humans living in proximity to sloths, particularly in rural areas of tropical regions, are at higher risk. This could make sloth fever virus outbreaks a serious public health concern if proper precautions aren’t taken.
Sloth Fever Virus Outbreaks
Historically, sloth fever outbreaks have been rare, but recent environmental changes have contributed to a spike in reported cases. These outbreaks, mainly localized in tropical rainforests, are linked to habitat destruction, which forces sloths into closer contact with other species and humans.
Real-Life Example: The 2021 Costa Rican Outbreak
In 2021, Costa Rica saw a small but worrying outbreak of sloth fever among sloth populations. Though no human cases were confirmed, scientists noted increased virus spread among wildlife, prompting stricter wildlife containment measures. This outbreak highlights the virus spread potential and serves as a cautionary tale for other regions.
| Year | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Costa Rica | Affected wildlife, no human cases confirmed |
| 2019 | Panama | Small outbreak in rural areas |
| 2018 | Brazil | Contained to wildlife populations |
Prevention and Containment of the Virus
Containing the sloth fever virus requires a multi-faceted approach. Since this is a wildlife-borne virus, preventing outbreaks means addressing both human-wildlife interactions and wildlife virus containment strategies.
Key Prevention Strategies:
- Habitat Protection: Reducing deforestation to minimize forced interactions between sloths and humans.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating populations living near sloth habitats about the dangers of close contact with wildlife.
- Veterinary Monitoring: Regular health checks of sloths in affected regions to detect early signs of outbreaks.
Local governments, wildlife agencies, and public health organizations must work together to prevent a larger-scale outbreak.
Sloth Fever Treatments and Vaccines
Currently, there is no specific sloth fever vaccine or antiviral treatment available. This is largely due to the limited number of documented human cases and the relatively recent discovery of the virus. However, researchers are working towards developing potential vaccines and treatments to prevent future outbreaks.
Possible Future Solutions:
- Antiviral Research: Scientists are exploring treatments that could mitigate the virus’s effects in sloths and potentially humans.
- Sloth Fever Vaccine Development: Though in its early stages, there are ongoing efforts to develop a vaccine for sloths, which could eventually be adapted for human use.
Conclusion
The sloth fever virus is an emerging threat that requires immediate attention from wildlife experts, public health officials, and governments in sloth-endemic regions. While the virus remains largely contained within wildlife, its potential to become zoonotic is a growing concern. Preventing future outbreaks will require robust wildlife virus containment strategies, public education, and ongoing research into vaccines and treatments.
-

 Sport4 months ago
Sport4 months agoIs Christie Sides Married? Exploring the Personal Life of a Renowned Basketball Coach
-

 Food5 months ago
Food5 months agoNew Restaurants in Canton, CT – 2024
-

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoSimone Biles Biological Parents: Understanding Her Journey
-

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoUnleash Your Potential at FBYANA Fitness Indonesia Gym
-
 Sport4 months ago
Sport4 months agoSimone Biles Husband Height: A Closer Look at the Athlete’s Power Couple
-

 Food5 months ago
Food5 months agoWhat Gives Amber Ale Its Sweet Flavor?
-

 Celebrity4 months ago
Celebrity4 months agoBianca Censori Spotted Shopping Solo in Beverly Hills: A Style Icon in the Making?
-

 Celebrity4 months ago
Celebrity4 months agoLarsa Pippen Before and After: A Deep Dive into Her Transformation Over the Years

















